
Without search engines, we wouldn’t be able to search the internet for terms and subjects of interest. These delicate mechanisms discover and classify web pages for us. And, of course, there are sets of rules they follow to provide the best results for our search intents. The main assistants in this vast and complex process, without which it wouldn’t even be possible, are crawlers. Crawlers navigate through websites and store information that later allows engines to properly index all types of pages. So, if you want your website pages to rank properly on SERPS, it’s necessary to understand how Google web crawling works.
Table of Contents
What Is Google Web Crawling?
Search engines are among the primary sources of fast and relatively relevant information. With crawlers, they play an essential role in organizing a large percentage of visible online content. Knowing how they work is vital for anyone who wants their website to rank higher in search results.
In general, there are three parts of the process that makes online searching possible:
- Crawling – Discovering content throughout links. Encompasses all pages and elements with links in them.
- Indexing – The second step is where search engines store and sort a vast amount of information they use when deciding what to serve to users.
- Serving – Organizing, evaluating, and displaying the most relevant results for search queries.
Google Web Crawling Process
Google uses Googlebot to visit new pages and gather information from the web. Often called crawlers, robots, spiders, or simply bots, they “crawl” through existing pages by travelling through links they find. However, this process is not random at all. It’s controlled and determined by Google algorithms, which give precise instructions about the crawlers’ behaviour. They define:
- which websites to crawl,
- how many pages to count,
- how often to search for updated information.
In addition, they also decide how to tackle the elements and scripts found on pages. But, most importantly, crawlers help gather information like metadata to help better index the pages later on. With this in mind, website owners, developers, and marketers must understand which things to focus on when creating or modifying a website. This understanding is crucial for allowing the website to rank high in SERPs.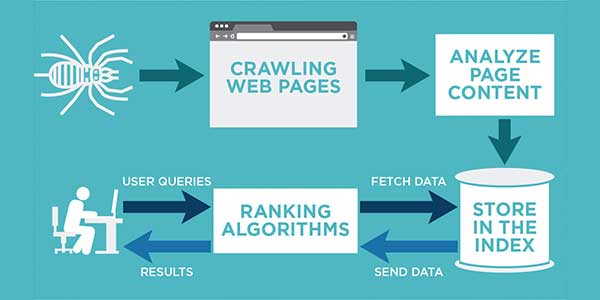
There Are Two Major Types Of Crawlers
While there can be many crawlers for a specific purpose, like ad crawlers or video crawlers, in general, we have two major types:
- Desktop crawler
- Mobile crawler
Depending on the type of website, Google decides which of the two will be used as a primary and secondary crawler.
For example, if you have a brand new website, you should focus on a mobile-first approach, mainly because Google prioritizes mobile-friendly responsive design for websites. With this in mind, Google will use the mobile crawler as a primary crawler for this website. But, the desktop crawler will also be used as a secondary crawler. The point is to see how well your website works on different devices.
Either way, crawlers simulate a user who is visiting a website. They follow the links and “fetch” essential information. And, at the same time, discover everything for when the time comes to rank websites in results.

What Pages Does Google Not Crawl?
There is one fact most people are not familiar with – crawlers do not crawl the entire existing internet. There are numerous factors to take into consideration before they decide if a page should be crawled. One of the most important is the number of links from other pages. Others include website traffic, information importance, speed, and specific demands. Here are a few examples:
- One of the best examples is pages blocked in robots.txt files. In most cases, crawlers will skip those pages.
- Crawlers will also pass pages that are not publically accessible. If there is an authorization process, like a login to access some pages, they are out of the crawlers’ reach.
- If there is no information update or request, already crawled pages won’t be crawled again.
- “Noindex, Nofollow” meta tags can be strong suggestions for crawlers to not index.
- Orphan pages – crawlers will not crawl pages without any links, nor will they appear in search results.
Bear in mind that crawlers don’t have to explicitly follow all these directives. In cases like Noindex, Nofollow, and robots.txt, they can opt-out of obeying the requests.
Improve Your Website Crawling Potential:
New websites have to ask search engines to crawl their pages by submitting requests on Google Search Console. This is the key step for websites that want to speed up the process of discovery and improve their online visibility. For this, there are numerous techniques:
- Creating and submitting a sitemap;
- Filing the crawl request for individual pages;
- Using only human-friendly URLs accompanied with a proper internal linking structure;
- Using the correct localization and language parameters to specify the alternate pages for different areas;
- Adequate use of robots.txt files to exclude sensitive or irrelevant pages from crawling;
- Optimization of different elements, especially those with links inside;
- Testing and evaluating your page rendering capability with a variety of tools.
Don’t Forget About Other Search Engine Crawlers:
Google is, without a doubt, the largest and most popular search engine. However, everyone who wants to improve their website’s online potential should consider other search engines as well.
- Bing – Bingbot crawler crawls websites using sitemaps. This crawler also respects URLs and content submission, together with quality links.
- DuckDuckGo – DuckDuckBot provides relevant search results while preserving security and privacy.
- Yahoo! – formerly the most popular search engine before Google stepped on the scene. They call their web crawler Slurp.
Keep tabs on how Google web crawling works and consider other search engines if you want the best possible results. Only with proper understanding is it possible to optimize a website and achieve satisfactory results. Even if the website is already ranking well, updating its content and other information will still require you to tackle web crawlers. At least, to speed up the entire process instead of waiting for it to happen “naturally”.

 About the Author:
About the Author:
















Be the first to write a comment.