
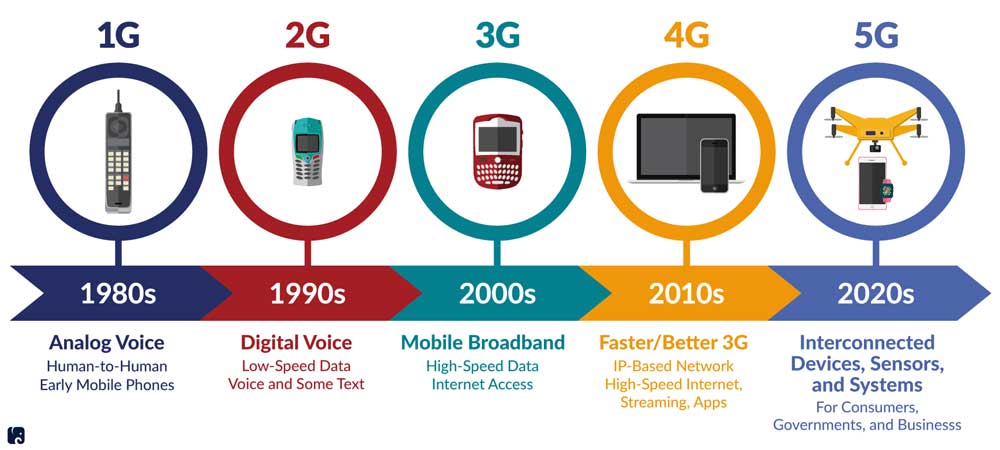
Going from 4G to 5G might not seem like a big leap, but the science behind 5G is actually light years ahead of 4G. Experts predict that 5G internet will drastically and forever transform how the economy and society functions on a global scale. Here are the crucial components that make the 5G network so much faster than 4G.
Table of Contents
5G New Radio Interface:
One of the reasons that 5G is so much faster than 4G is the 5G New Radio interface. This technology runs on a significantly higher frequency than 4G, increasing from 700 MHz in older technology to over 28 GHz in 5G. That is a 40-fold increase in speed, which is indeed a game-changer in terms of what can be accomplished by way of internet connection.
5G is so much quicker than 4G that surgeons working in China recently completed brain surgery that was performed entirely over a 5G connection. Further innovation in terms of how to apply the faster data transfer speeds of 5G into practical use is in development.
RF Amplifier:
Radio frequency amplifiers, or RF amplifiers, a technology new to the mass market, can exponentially boost radio signals, turning a weak, distant one into a powerful, more usable signal using millimeter wave spectrum.
With the aid of an RF amplifier, internet users can achieve tremendous gains in the signal level without additional “noise” from the airwaves. This keeps the all-important signal-to-noise ratio in check and keeps the signal clear.
Multi-User Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MIMO):
Massive MIMO networks differ from standard MIMO networks by volume of antennae. While older MIMO networks have only a small handful of antennae, the massive (or “multi-user”) MIMO networks used in 5G have upwards of several hundred antennae.
Like RF amplifier technology, massive MIMO boosts the signal-to-noise ratio as well as offering increases in throughput. MIMO advances offer boosts to speed and coverage of localized sites.
While 4G can only support about 4,000 devices in a local area, the data shows that 5G can support more than a million using massive MIMO networks.
Internet Of Things (Nanotechnology):
The concept of the Internet of Things (IoT) is the increasing physical connectivity of objects in the world with chips, sensors, and other nanotechnology devices that facilitate the input and output of information.
The technologies that 5G rely on enable a new level of connection that was previously unimagined. The potential uses of this new capability in the IoT are nearly endless. Including AI-driven healthcare, job automation, and smart home security systems.
We have only begun to witness the transformations that 5G will cause in the society and economy as the rollout continues. Experts estimate that by 2024, nearly half the world population will have regular access to 5G networks.

 About the Author:
About the Author:















Be the first to write a comment.