
Businesses and individuals are shifting towards cloud computing to store their documents for safekeeping and greater accessibility. Cloud computing is the 21st-century solution to the filing room, minus the additional costs of storage, security, etc. Cloud-based storage systems are becoming an invaluable resource for businesses, and the following stats prove them:
- There were around 3.6 billion cloud users in 2018 (Source: Statista)
- The number of cloud users soared by 50% between 2013 to 2018 (Source: Statista)
- 73% of businesses have at least a part of their enterprise computing infrastructure or one application in the cloud (Source: 2018 IDG Cloud Computing Study)
Table of Contents
Exploring Cloud Computing And Storage:
A cloud-based storage system is a cloud computing service model where data can remotely be backed up, stored, and managed by users through the internet. Cloud-based storage architecture models can be of three types – public, private, and hybrid.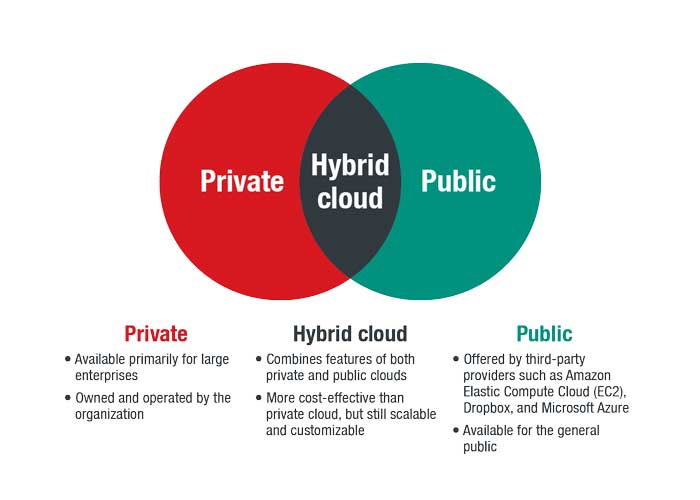
Types Of Clouds:
Public Clouds:
Public clouds provide their services to individual users and firms over the internet. Their services can be enjoyed by anyone who pays a fee and has a functional browser. Despite being a public cloud, the data of individual accounts is safe through encryption. Some popular examples of public clouds are Windows Azure, Google AppEngine, Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2), and IBM’s Blue Cloud.
Private Clouds:
Private clouds are created by firms and entities to store and maintain their internal data and documents, including employee records, trade secrets, and more. The cloud infrastructure, servers, and hardware are owned or maintained by the cloud. A few examples are Dell EMC’s Oracle and Hewlett Packard Enterprise’s Helion.
Hybrid Clouds:
Hybrid cloud solutions are usually employed by organizations that use both public and private clouds to store and manage their data. The company’s sensitive and confidential data is stored in private clouds, but the more general information such as consumer reports are kept in the public clouds.
Users can access their data from anywhere they want at any time they want. All they need is an internet connection and a device.
While cloud systems appear simple from the users’ perspective, there are multiple layers of protection added to them to secure your data. Other than adding a password to access the cloud, cloud-based storage systems have more levels of security.

Cloud Firms’ Efforts At Security:
Advanced Firewalls:
Firewalls inspect the outgoing and incoming data packets (i.e. destination data and source) to decide which network traffic to block or allow based on established security rules. Advanced firewalls verify packet content integrity and map packet content. They create a barrier between the secure internal networks and outside networks like the internet.
Encryption:
Encryption of the data keeps it safe from unauthorized users. If an encrypted file is stolen, it cannot be accessed without a key.
Internal Firewalls:
There are internal firewalls to limit access to the account in the data cloud. Secure cloud access will boost security as a compromised account will not get full access.
Intrusion Detection:
Cloud systems have multiple detection levels in place to identify any intrusion or break-ins from unauthorized parties who have passed through the initial defenses of the network.
Event Logging:
All network actions are recorded in events logs. Event logs are viewed by security analysts to build a narrative of network events to predict and thereby prevent possible security breaches in the cloud.
Physical Security:
Cloud storage facilities have the utmost level of security, including armed guards, 24-hour CCTV monitoring, and biometric locks.
Cloud systems use all or most of these security measures to minimize the risks of thefts and breaches, so the data is secure.
Risks And Breaches:
Clouds are at constant risk due to the nature of the information present in them. According to the Cost of a Data Breach Report, global data breaches have cost companies an average of $3.86 million. Therefore, it is important for cloud providers and firms to ensure that the highest levels of security are in place.
The high risks have the users constantly concerned about their data and privacy. According to Cloud Vision 2020: The Future of the Cloud survey, around two-thirds of organizations are hesitant about employing cloud storage due to security concerns. Furthermore, the survey showed that compliance, governance, regulatory, and privacy concerns of the cloud have 60% of the firms worried.
Aside from data breaches, there are many other risks associated with the cloud. Some of which are stated below.
Risks Of Cloud Storage:
- Data breaches
- Insider threats
- Human error
- Account hijacking
- Insecure Interfaces and APIs
- DDoS (Distributed denial-of-service) attacks
- Advanced persistent threats
- Weak Control Plane
- Data loss with no backup
- Abuse and Nefarious Use of Cloud Services
- Spectre & Meltdown
- Limited Cloud Usage Visibility
- Metastructure and Applistructure Failures
- Insufficient Identity, Credential, Access, and Key Management
- Lack of Cloud Security Architecture and Strategy
- Misconfiguration and Inadequate Change Control
Keep Your Data Secure
Apart from the security checks and measures that are set in place by the cloud service providers, the users themselves can take certain actions to ensure that the data in their cloud is safe and secure.
Tips To Secure Data In Cloud System:
Below are a few tips you can employ to secure your data in cloud storage.
Make Passwords Stronger:
Create hard to hack passwords that include different letters, numbers, and even a few punctuations. Change your passwords regularly for greater security. Also, avoid keeping your birthdate, nickname, spouse’s name, or any other obvious bit of information as your password.
Backup Data Locally:
Don’t just depend on cloud storage. Although cloud providers take several security measures. Still, there are chances of data hijacking or completely erasing the data. Therefore, it is wise to make a backup and keep it in a secure location.
Use Cloud Services that Encrypt Data:
Use a cloud service provider that has data encryption, so even if your data is stolen, it cannot be accessed or viewed without a security key.
Encrypt Your Data:
Keep encrypted data in your cloud for extra protection so your data is as good as useless for any unauthorized users who might get their hands on it.
Avoid Storing Sensitive Information:
Do not store any sensitive information in your clouds like trade secrets, identification documents, or any data that might cost you. Private clouds are then again safer than public clouds. However, keep your cloud storage for turnover reports, research material, consumer insights, photographs (no nudes though), and other general information.
Install Anti-virus Software:
Install an antivirus to detect any threats or risks in your cloud, and to block any penetration points that hackers might try to access. A good antivirus will render their attacks ineffective o keep your data safe and your system impenetrable.
Test the Security Measures in Place:
Try accessing your data without inputting any authorization details and get a hacker friend to try to breach the security for cloud testing. If you can penetrate the cloud, then it is definitely at risk of getting hacked from professionals. Getting a friend to hack your cloud will allow you to identify loopholes and security threats. You can later discuss these with your cloud provider or can fix them in your private system.
Conclusion:
While cloud technology may appear to be safe, clouds are still at risk. However, this storage opportunity does save space and cost. Nonetheless, it is a good idea to take certain measures on the individual user level too to make sure your data is safe.

 About the Author:
About the Author:












Be the first to write a comment.