A data center is much more than a building with a bunch of computers and high electricity costs. Today information storage and transmission have become of grave importance – we all depend on data centers despite our different backgrounds and different needs.
If you still lack knowledge about what a data center is and what it’s used for, I can explain. A data center is a facility used to house multiple servers, loaded with huge amounts of data. The information they hold is used by billions people, institutions and companies worldwide. Data centers play an important role not only holding the data, but they also preserve it and ensure constant flow and exchange of information.
Thus the performance of the data centers is really important for every single one of us – no matter whether you’re playing some Xbox game online, trying to log in to your bank account or setting up a website about kittens. Let’s take a closer look at the data centers and learn something new.
Table of Contents
From Greenland To New Zealand:
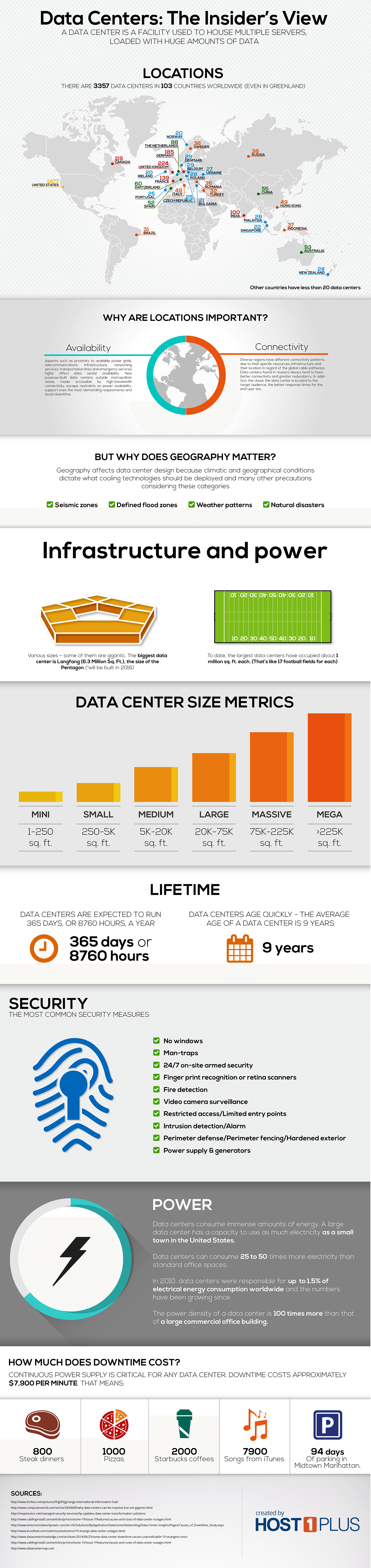
To date, the total number of the data centers has topped 3K. Being scattered worldwide, some of them are far-off the global network pathways. However, because of the growing demand of the global community the amount of the data centers worldwide has increased significantly and global network is spreading to distant regions as well.
More and more data centers are mounted in the North. Due to the nature of a data center, the upkeep of the server environment is less expensive when collocations are placed in the colder regions. Cooler climate means lower energy/electricity costs OR lesser power demand. Cooling makes .. percent of an average data center costs, while in a colder climate there is less or no need for artificial cooling mechanisms – cold air is blown directly from outside. Iceland, for example, has lower electricity costs as much of the energy is generated by carbon-neutral technologies, including geothermal and hydro-electric power.
Why does the location matter? Data center placement has high importance for both the company and the back end user. The first and the most well-known reason is this – the location influences the loading times of any online material – the closer the data center is located to the target audience, the better response times are.
Moreover, the selection of a particular location leans on the local conditions – the proximity to available power grids, telecommunications infrastructure, networking services, transportation lines and emergency services.
However, infrastructure is not the only parameter that needs to be taken into account while talking about the importance of data center locations. What often remains forgotten is the impact of different climatic and geographic conditions and their shifts. Thus areas in active seismic zones, potential flood zones, regions with extreme weather patterns or at risk of natural disasters are in constant danger and at higher risk of blackouts. Not only climatic and geographical conditions always dictate the precautions and specifics of data center designs, particular locations at constant risk are usually avoided. Of course, political and economical stability is of quite importance as well.
A Closer Look:
Data centers vary significantly in both size and amount of servers they hold – a range from single-server home-based data storage sites to massive building complexes with additional maintenance facilities. Most of the large-scale data centers cover about 1 million sq. ft. each. If you think that’s a lot, wait until you hear about the largest ones.
The biggest data center is considered to be Langfang – a 6,3 million sq. ft. gigantic facility, scheduled to launch in 2016. Being the size of the Pentagon, this data center is expected to surpass all existing data centers. However, not for long – by 2019 or 2020 Microsoft is planning to build a major facility in Iowa, much more than 6 million square feet in size.
Still, despite the size, most data centers are quite ephemeral – the average age of a data center is 9 years and they tend to age really quickly. Thus most data centers need constant upkeep and renovation. According to 2013 Uptime Institute Data Center Industry Survey, over the past 5 years 70% of data center operators had to build a new site or renovate the old ones.
Harder, Better, Faster, Stronger:
From the physical point of view, most data centers might resemble of immense strongholds. If you are aware of their immaculate security measures, faultless infrastructure, carefully measured designs, highly trained on-site staff and highly-monitored chambers for the servers, you would find no other words to describe them.
While on site, each facility takes precautions to preserve the servers from many of hazards from environmental and power failures to security breaches.
- Air conditioning is necessary as the electrical power used heats the air.
- Recommended temperature is 18–27 °C (64–81 °F).
- Maximum recommended humidity is 60%.
- No food, no drinks, no smoking, no touching!
You might find these environmental conditions ordinary, however, maintaining a reliable environment for the servers is one of the trickiest and most important tasks. Also it highly affects the costs of any data center. For example, cooling makes up around 30% of total energy usage in an average data center. Quite a lot, huh?
As for security measures, most centers use both advanced technologies and traditional means to minimize the possibility of a potential breach. The most common methods include on-site security guards, intrusion detection, man traps, video camera surveillance, motion detection and more. Also, while each data center is built, the design is created having security in mind – the new data centers are not likely to have windows and are designed to be accessible by human staff as less as possible. And there’s a good reason why.
And It’s Gone:
Data center outages are rare, if compared to the chances of a single server failure, but they can happen anyway. And they do! According to Emerson report, in 2013, the average overall outage time (both partial and total) was 86 minutes.
What may cause a data center outage? The most common causes are pretty easy to guess – IT equipment failure, environment failure, generator failure, natural disasters & extreme weather. But the most common cause of downtime is human error. Think whatever you want, but machines are less likely to mess up by themselves.
And yet unbelievably strange things can happen as well. For instance, squirrels might be quite of a problem – their “chew it all” philosophy often has consequences, as squirrels seem to damage the wires, thus causing partial blackouts and downtime. You don’t believe me? In 2010 some squirrel took out half of our Santa Clara data center.
Furthermore, to save the data center in Oregon, Google is building underground pathways for their wires, as each November when the hunting season begins their wires are ALWAYS shot down.
If you think this is funny, have in mind that there are hundreds of such stories – from anchors dropped on intercontinental cables to drunk truck drivers, crashing the facilities.
However, the consequences of data center outages are quite serious – downtime always means lost revenue, lost productivity and sometimes, even data loss. It is calculated, that by 2013 the average cost of each minute of downtime has reached about $7,908 , although it slightly differs depending upon a specific data center.
I really hope that you have discovered new interesting facts about data centers! Have anything in mind that wasn’t mentioned above? Please share your thoughts!
This Infograph is shared here after legal permission from Host1Plus


















Be the first to write a comment.